Credit basics
Credit report:
A credit report is a statement of your credit activity. It contains personal information (name, addresses, date of birth, SSN etc.), credit information (current and old accounts, type of accounts, payment history, credit limit etc.), and other records (foreclosures, bankruptcies, liens etc.). Elements in your credit history such as payment history, types of accounts, credit usage, and others, have the ability to impact your credit score and credit rating.
Credit score:
A credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness. It is a number that falls in the range 300 – 850. The higher your number, the better it looks on loan applications. Your credit score is based on your credit history. It’s based on factors listed in your credit report. This includes information such as how many accounts you have, how much debt you have, what your repayment history is like, and more.
Credit rating:
Feature creep get six alpha pups in here for a focus group, or those options are already baked in with this model loop back please submit the sop and uat files by next monday so shotgun approach.
In short, a credit score is a number that reflects your credit history. Understanding your credit report can feel overwhelming, but we can make it simple to understand.
This article looks at:
- The definition of a credit score
- How credit reports are used
- What is considered a good or bad credit score.
- Why credit scores are important and how they are calculated
Hopefully with this guide you will feel confident in understanding your credit score and credit report
What is a credit score?
A credit score is a number that reflects your credit history. It may only be three numbers, but it can say a lot about your past loan history.
Your credit score is a combination of your loan and credit history. It gives lenders an idea of how likely you are to pay off a loan.
A higher credit score shows that you have a good history of paying back your loans and managing debt well. A lower score shows that you do not have the best history of paying back loans on time. Most creditors and loan agencies are looking for a higher credit score. Usually, a credit score of 700 and above is considered a good credit score. A score of 800 and above is considered an excellent credit score.
There are many different types of credit scores, but the two most popular ones are the FICO score and VantageScore. Most companies look at your FICO score, so we will focus on that. We will, however, discuss the difference between the FICO score and the VantageScore a little later.
Your credit score number can range anywhere from 300 to 850. That number is determined by many factors, all of which make up your credit report. Factors include:
- Payment history
- Amount owed
- Credit utilization
- Length of credit history
- New credit
All of the above factors contribute towards your credit report.
Your credit score considers the amount of credit you have out, what your payment history looks like, and how many accounts you have.
Of course, sometimes life happens, and your credit score is hurt. There is no shame in having one credit score or another. The only issue is that having a good credit score can open more loan and credit opportunities. Remember that having access to loans is a good thing.
Almost everyone has debt of some type. You need loans to buy a house, car, or get a credit card. Your credit score is vital to determining if you get approved for a loan.
If you want to improve your current credit score, you will have multiple options on how to work on improving it. Credit scores are important. They can have a big impact on the financial resources you can access.
Understanding your credit report
Your credit report is an ongoing display of your behavior with credit. It’s a lot like a report card that makes up your overall credit score. A credit report is created from a combination of factors including information provided by different financial institutions. Some of the institutions include:
- credit card companies
- home and auto loan providers
- banks
- utility companies
- student loan lenders
Depending on what services you have, your report can also reflect your history of rent, utilities, and even cell phone bill payments.
There are several credit bureaus that report your credit activity. However, three main companies that matter the most: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. Each bureau has a score for you. Those three scores combine to determine your FICO score.
Along with your score, your credit report may have other information as well. It may show your name, date of birth, social security number, and address. Your credit report does not display your employment history or day-to-day purchases.
When applying for credit, creditors will take a look at your report. Your credit score will tell them how likely you are to pay back a loan. Creditors are trying to determine your creditworthiness. The better your credit report, the better chance you have at getting approved.

Credit report vs credit score
A credit report is a detailed record of your credit activity. The information on your credit report is used to generate a 3-digit score between 300 and 850 which is your credit score. Your credit score is what qualifies or disqualifies you from getting a loan, or mortgage, approval for a new credit card, and other important things. It is a measure of how likely you are to repay.
How is your credit score calculated?
The majority of the information on your credit report comes from the credit bureaus Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. All year round, credit agencies and financial institutions are sharing information with these three credit bureaus. They are providing information on who is paying back their loans, who is applying, and more. All of your financial institutions report your credit information to the credit bureaus.
Here is a list of some information they report:
- Account balance details
- Amount borrowed
- Amount paid
- Status of your account
- If you apply for debt
This list is not all-inclusive, but it contains a lot of the main information they send.
What factors affect your credit score?
Payment history, credit utilization, age of credit, credit mix, and credit inquiries all affect your credit score.
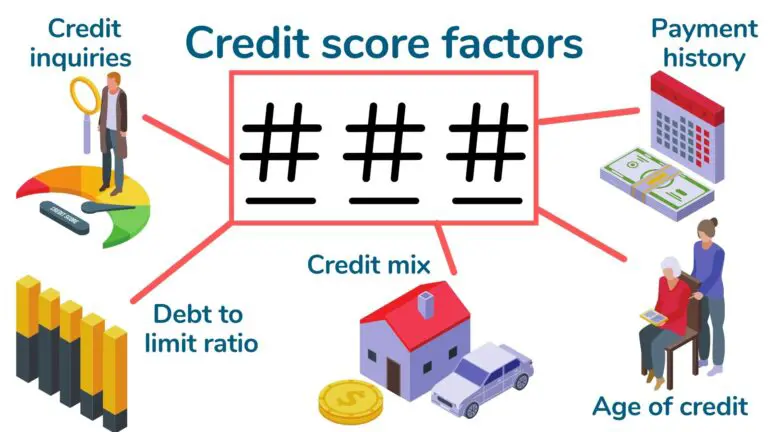
Payment history
Your payment history impacts your credit score the most. It shows how well you are about making consistent on-time payments. One or two late payments can hurt your score. Having multiple late or missed payments could cause lasting damage. Paying your bills back late, or not at all, are two of the fastest ways to hurt your credit.
Credit utilization
The next most important factor is credit utilization, or debt-to-limit ratio. This ratio looks at the limit of your credit and compares it to how much debt you actually have. For example, if your credit card has a max of $5,000, how much are you actually borrowing? Only taking out $1,000 at a time and paying it back would look better than taking out the full $5,000. The lower the number, the better impact it has on your score. The idea is that you are living within your means. Lower credit utilization shows you are not solely relying on credit to make payments. If you are looking for that magic number, many experts recommend keeping the ratio below 30%. The good news is that you can improve this number either by increasing your credit limit or paying down debt.
Age of credit
Next is the age of credit. This factor shows how long you have had credit in your name. It looks at how long you have had debt, as well as the age of specific accounts. Along with looking at how old your account is, it also looks at how much time has passed since you last used your account. Having a longer credit history will improve your score. If you find that you can manage your credit pretty well, you might want to consider not closing credit cards. Instead, you might want to keep your first credit card open and just occasionally use it to make small purchases. Using it to make small purchases here and there will keep it active.
Credit mix
The fourth factor on this list is credit mix. This factor does not impact your score nearly as much as payment history, credit ratio, or age of credit. This looks at how many different types of accounts you have. Do you have credit cards, school debt, auto loans, mortgage, and other types of credit? Surprisingly enough, having multiple types of credit accounts can improve your score. Having active accounts shows that many lenders have approved you. It also shows that you can pay off multiple loans at the same time.
Credit inquiries
Credit inquiries affect your score the least, but you should still be cautious because they can sneak up on you.
The good news is that you do not have to worry about every credit inquiry. There are two different types of inquiries, and only one affects your score.
Hard credit inquiries
Hard inquiries are from financial institutions (like a bank or credit card company). The companies submit a hard inquiry when you apply for a loan with them.
That is why it is not a good idea to blindly apply for loans that are likely to deny your application. When you apply with a lot of places, they all submit credit inquiries, which hurts your score. Inquiries might only affect your score by a couple points, but it can add up quickly. This means that the next company to do a credit inquiry will see an even lower score. When you have a lot of hard inquiries, it looks like you are desperate for money.
Soft credit inquiries
The other type of inquiry is a soft inquiry. Some companies need to see your report as part of their background check. The good news is that credit inquiries do not impact your credit score.
Oftentimes, potential landlords and employers will submit a soft inquiry. Some payday lenders do a soft credit inquiry too. Companies that do a soft credit check are often trying to confirm your identity. They want to ensure that you are the person you say you are.
The difference between the FICO score and VantageScore
FICO has been the most popular credit score for years. However, VantageScore is also growing in popularity. For the most part, the difference between these scores will likely not affect you, but they can both help with different needs and goals. Overall, there are pros and cons to both scores. Which score you, or others use, is up to the individual, but for now we will list some of the similarities and differences.
FICO collects your credit scores from the three credit bureaus and then analyzes it. VantageScore looks at consumer credit files instead to build your score. Both types of scores use the same range of numbers. Their scores range from 300 to 850. If you do not have a credit history, you might want to keep a closer eye on your VantageScore. FICO requires a good six months of information. The VantageScore only needs a month of credit history. You could have a VantageScore before you have a FICO score.
The two scores both decrease when you have missed or late payments on accounts. The difference though is that FICO ranks all late payments of equal importance. VantageScore ranks some late payments as more important than others. For example, a late mortgage payment is penalized more than others. The tradeoff is that FICO and VantageScores look at collection activity differently. Having an account go to collections can hurt your score. However, FICO ignores collections that had an original balance less than $100. VantageScore does not dismiss these.
Another difference comes from credit inquiries. We talked earlier about hard checks and soft checks to credit. A lot of times, when you apply for an auto loan, your application is sent to several lenders over the course of a few days. Rather than dinging your score with each of these checks, the credit companies only ding your credit score once so long as the hard checks are only within a few days of each other. The difference though is that FICO has a 45-day window and VantageScore has a 14-day window.
Credit score range
Credit scores go on a range. Every item that requires a credit score will have a range that they want. Of course, as we have mentioned earlier, there is no shame in one credit score over another. Certain ones will open more doors. Other credit scores may mean you are denied on more applications.
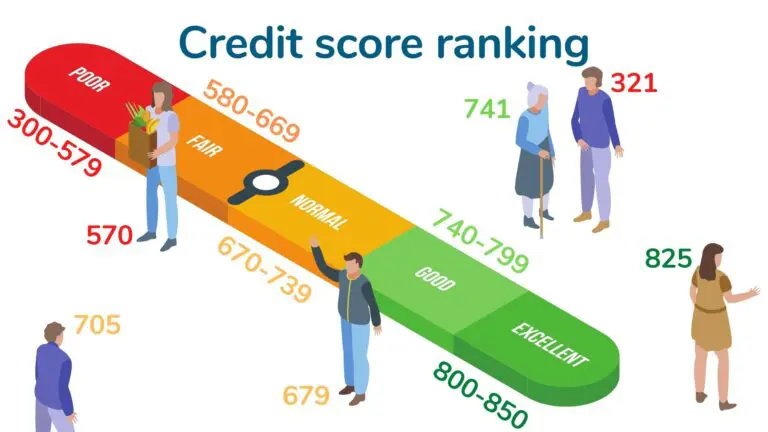
Credit scores range from 300 to 850. They also range from being ranked as poor to excellent. Below we have the average FICO score range.
- Excellent: 800 to 850
- Very Good: 740 to 799
- Good 670 to 739
- Fair: 580 to 669
- Poor: 300 to 579
Please remember that your credit score ranking is not a reflection of you. It is only a reflection of your credit history. It just says that you do not have the best history of paying back debts or might be swimming in credit card debt.
Knowing the ranking system is only one part of the equation. You probably want to know what your credit score looks like in the big picture. You might have questions about what score you need for credit applications. Are you more likely to get access to great loan rates? What credit card perks do you qualify for? You might also be wondering how your score ranks in comparison to others.
Did you know that about 30% of Americans have a credit score of 600 or less? So, if your credit score is sitting in the fair or poor ranking, do not fret. You are not alone.
Using numbers for your credit score can provide a lot of information in one glance. For example, it could alert you that your identity might have been stolen. If your credit score seems off, too low or too high, be sure to look over your report. Look for inaccurate information. It might be affecting your score.
If you need money and are struggling to get approved, consider a payday loan. There are loans with no hard credit check that can help during difficult situations. They are great for people with no credit or bad credit. They are simply here to provide financial relief to those who need it. We know life happens, so regardless of your credit history, if you need a small loan now, you can apply at Net Pay Advance!
Why is your credit score important?
Credit checks and loan approvals
Your credit score helps you get approved for loans, credit cards, apartments, and more.
If you apply for a credit card, that company will check your credit score. Loan providers will check your score to see what your credit history has looked like over time. They will use that information to determine your likeliness of paying off debt with them.
It is not just lenders and financial institutions that look at your credit score. Other companies look at your score as well. If you apply for an apartment or a cellphone contract, they may need to check your credit score too. They want to check how likely you are to make on-time payments. Employers will also look at your credit score. Often they check as part of their background check to make sure that you are the person you say you are.
Interest rates
Not only will your credit score determine if you are approved for a loan, it can also affect the amount you pay. If your credit score is low, you might have to pay higher interest rates. If your score is better, you might qualify for better credit card deals. This may mean having access to cash back programs, lower APR, or even airline miles. Having a very good or excellent credit score can really help open doors. Having a fair or poor credit score can make life difficult. Credit scores are incredibly important when it comes to getting approved for credit or loans.
Will a payday loan affect my credit score?
One common question we hear a lot is if a payday loan will affect your credit score. The short answer is no. The long answer is it only will affect your score if you do not pay and your debt goes to a third-party collection agency. Even then, it will only be reported if that third-party company chooses to report it. At Net Pay Advance, we do not look at your credit score when you apply. In return, we do not report your payment history. For a more in-depth explanation, check out our super helpful credit score FAQ article here.
There are several ways to improve your credit score. If you want to build up your credit, it is possible, regardless of where your score is now.
Hopefully, this guide did a great job of answering any and all of your credit-based questions. However, we realize that nothing can be completely all-inclusive. Do you still have a question about credit? Feel free to leave a public comment below and we will be sure to answer.
This blog was originally posted September 29, 2019 and has since been updated.
